Linux #
Set a static IP for a network card on AWS Linux/Centos #
File: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
HWADDR=<MAC_ADDRESS>
TYPE=Ethernet
BOOTPROTO=none // turns off DHCP
IPADDR=192.168.2.2 // set your IP
PREFIX=24 // subnet mask
GATEWAY=192.168.2.254
DNS1=1.1.1.2 // set your own DNS
DNS2=1.0.0.2
DNS3=9.9.9.9
DEFROUTE=yes
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
NAME=eth0
DEVICE=eth0
ONBOOT=yes // starts on boot
Set a dynamic IP for a network card on AWS Linux/Centos #
File: /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
HWADDR=<MAC_ADDRESS>
TYPE=Ethernet
BOOTPROTO=dhcp
DEFROUTE=yes
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no
NAME=eth0
DEVICE=eth0
ONBOOT=yes // starts on boot
Set global DNS/Gateway on AWS Linux/Centos #
File: /etc/sysconfig/network
GATEWAY=
View current DNS server address #
cat /etc/resolv.conf
View current Gateway #
ip route | grep default
Ifconfig shows ens instead of eth #
- Icfg files are not picked up by their MAC address!
- Name the files as ifcfg-ens33
- Remove the mac address from ifcfg files
- Set the DEVICE in ifcfg to ens33
Change hostname #
For non AWS Linux #
To view current hostname
hostname
To change hostname
nano /etc/hostname
nano /etc/hosts
Change hostname on AWS Linux #
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/set-hostname.html
Restart the linux networking service #
service network restart
or
sudo systemctl restart network
Check if network port is open on Linux #
echo > /dev/tcp/google.com/80 && echo "Port is open"
Install redis on AWS linux #
sudo yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
sudo yum --enablerepo=remi install redis
sudo nano /etc/redis/redis.conf
- Comment line “ bind 127.0.0.1 -::1”
- Change protected-mode to no
sudo chkconfig redis on
sudo service redis restart
Install nvm on linux #
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.1/install.sh | bash
Zip on linux #
zip -r destination.zip sourceDir
Unzip on linux #
unzip filename.zip -d /path/to/directory
Time how long a command takes on linux #
time <command>
Disable firewall on linux #
sudo systemctl stop firewalldsudo systemctl disable firewalld
Yum - updates commands #
- Install all updates using yum
yum update
- List packages to update using yum
yum check -updates
- List installed updates using yum
sudo yum history- OR
sudo cat /var/log/yum.log
- Undo/rollback/revert an installed update using yum
yum undo <transaction_id>
- Install only security updates using yum
yum update --security
- Install only bug fixes using yum
yum update --bugfix
- Update specific package using yum
yum upgrade <package>
View details about a running process on Linux #
ps -p <PROCESSID> -o pid,vsz=MEMORY -o user,group=GROUP -o comm,args=ARGS
Find files of specific extension on Linux #
find . -type f -name "*.html"
Copy files of specific extension on Linux #
find . -type f -name "*.html" -exec cp --parents {} ./destination \;
Find a string in multiple files on Linux #
-
grep -rn '/path/to/somewhere/' -e 'pattern'-ror-Ris recursive,-nis line number, and-wstands for match the whole word.-l(lower-case L) can be added to just give the file name of matching files.-eis the pattern used during the search- Along with these,
--exclude,--include,--exclude-dirflags could be used for efficient searching:
-
Exclude a directory from find
grep -rn '/path/to/somewhere/' -e 'pattern' --exclude-dir testdir
Convert EOL/EOF line endings for entire directory #
- On a linux machine (or WSL) install dos2linux
sudo apt install dos2unixfind . -type f -name '*.ts' -print0 | xargs -0 dos2unix
- The same applies to the unix2dos
View free memory on Freebsd #
dmesg | grep memoryfree -m
Mysql settings file (for changing memory settings) #
etc\my.cnf
Block an IP address on Linux #
iptables -A INPUT -s IPADDRESS -j DROP- http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/how-do-i-block-an-ip-on-my-linux-server/
Block a subnet on Linux #
iptables -A INPUT -s IPADDRESS/SUBNET -j DROP
- i.e.
sudo iptables -A INPUT -s 183.181.204.0/255.255.255.0 -j DROP
Remove a rule from IP tables on Linux #
Same as add but with -D instead of -A
iptables -D INPUT -s IPADDRESS -j DROP
List ip table rules on Linux #
sudo iptables -S
View high CPU processes on Linux #
top
- To modify the output of top command
- Type ‘i’ to remove the idle processes from the display.
- To revert back type ‘i’ again.
- To sort the data by memory usage type ‘M’
- To sort by how long the processes have been running type ‘S’ and type ‘P’ to sort by CPU usage again.
- It is also possible to modify the processes from within the top command.
- Type ‘u’ to view processes owned by a specific user
- Type ‘k’ to kill processes and ‘r’ to renice them.
- %CPU column – CPU Usage
- The percentage of your CPU that is being used by the process.
- By default, top displays this as a percentage of a single CPU.
- On multi-core systems, you can have percentages that are greater than 100%. For example, if 3 cores are at 60% use, top will show a CPU use of 180%. - You can toggle this behavior by hitting Shift-i while top is running to show the overall percentage of available CPUs in use.
References
Give full access to a file on Linux #
chmod 777 <FILE>chmod -R 777 <DIR>
Change owner on Linux #
chown user <FILE>chown user:group <FILE>chown -R user:group <DIR>
Find apache current dir on Linux #
httpd -V
Find last boot time on Linux #
who -b
View Path on linux #
echo $PATH
How to get the size of a directory on linux #
du -sh <DIR>
How to get the size of current files and subdirectories on linux #
du -sh ./*
Login as a different user #
su - USERNAME
Linux Tips/Cheat sheets #
Learn Linux (fast): 30 commands for beginners (with cheat sheet) - from hackthebox.com
Linux networking commands #
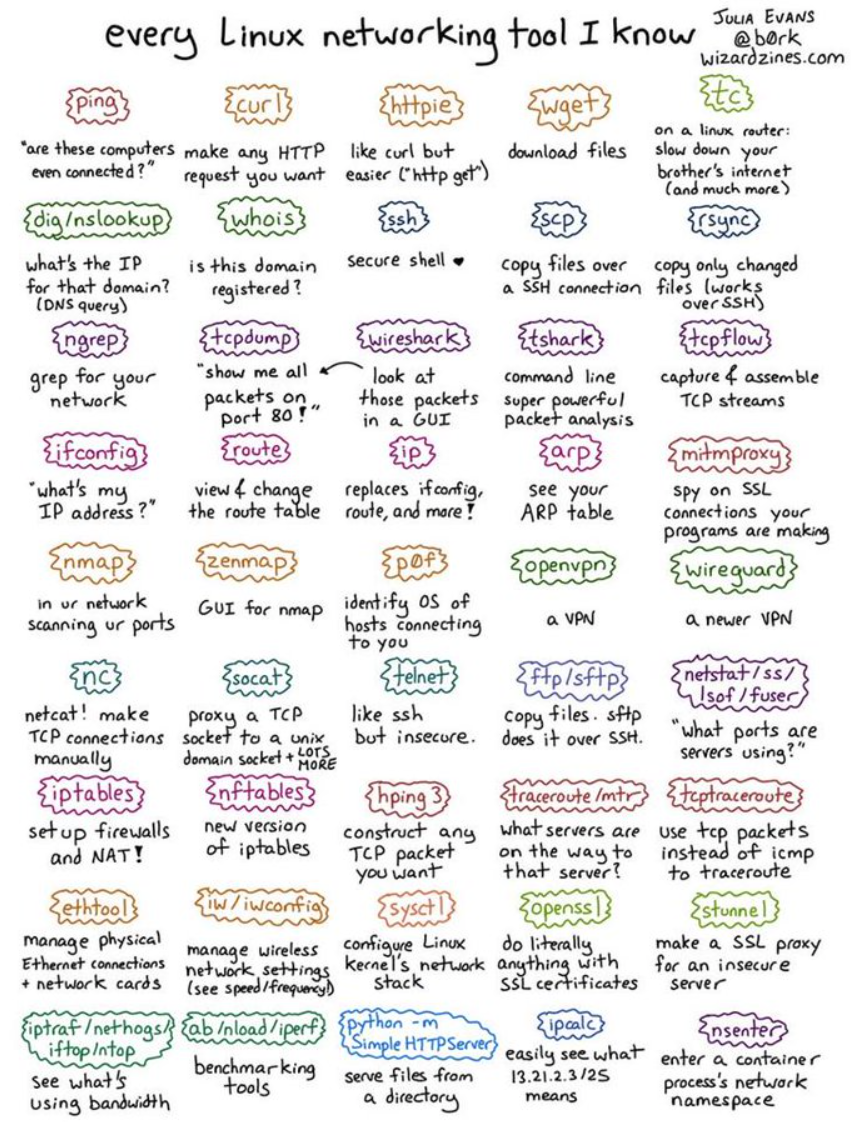
by Julia Evans
View current Amazon Linux version #
cat /etc/os-release
grep -E -w 'VERSION|NAME|PRETTY_NAME' /etc/os-release
Remi RPM repository installation instructions #
https://rpms.remirepo.net/wizard/
Remove an RPM repository (CENTOS 7) #
- Find the exact installed repo name
rpm -qa | grep epel - Remove it
sudo yum remove epel-release-7-14.noarch
Instal httrack on fedora/centos amazon linux #
- Download the latest linux sources version of httrack (https://www.httrack.com/page/2/)
tar xvf <downloaded-file>.tar.gzsudo yum install openssl-devel zlib-develsudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools"- Move to the directory containing the source of httrack
./configuremakesudo make install
Extend disk space inside a linux vm after vmware host disk resize #
To resize a partition, you actually “delete” it and then add a new one with the new size, making sure to place the beginning of the new partition at the same sector/cylinder as the old one started. This process is NOT destructive, your data still remains on the disk. These first steps are for deleting the partition:
- The fdisk command provides disk partitioning functions and using it with the -l switch lists information about your disk partitions. At the command prompt type fdisk -l
- The response should say something like Disk /dev/sda : xxGB
- At the command prompt type fdisk /dev/sda. (if dev/sda is what was returned )
- Type p to print the partition table and press Enter
- Type d to delete the last partition
- Type the number of the last partition
- Type n to add a new partition
- Type p again to make it a primary partition
- Now you’ll be prompted to pick the first cylinder which will most likely come at the end of your last partition
- If you want it to take up the rest of the space available, just choose the default value for the last cylinder.
- Type w to save these changes
- Restart the VM
- pvresize /dev/sda2
- lvextend -r -l +100%FREE /dev/mapper/centos-root
Work with multiple terminals in linux using ‘screen’ #
Screen is used to create a new ‘screen’ session, each screen session can have multiple windows
- Start a screen session:
screen - List all screen sessions:
screen -ls - Connect to a screen session:
screen -r <ID> - Detach from a screen session:
Ctrl+D - While in a screen session
- Create a new window:
Ctrl+A C - List all windows and switch between them:
Ctrl+A " - Create a split:
Ctrl+A S - Switch between splits:
Ctrl+A Tab - Remove current split:
Ctrl+A Q
- Create a new window:
Permissions #
Binary, Octal, String Representation, and Permissions #
| Binary | Octal | String Representation | Permissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 000 | 0 | — | No Permission |
| 001 | 1 | –x | Execute |
| 010 | 2 | -w- | Write |
| 011 | 3 | -wx | Write + Execute |
| 100 | 4 | r– | Read |
| 101 | 5 | r-x | Read + Execute |
| 110 | 6 | rw- | Read + Write |
| 111 | 7 | rwx | Read + Write + Execute |
Example #
| Owner | Group | Other |
|---|---|---|
| rwx | rw- | r-x |
Example Owner Permissions Breakdown #
| Permission | Symbol | Value | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Read | r | 4 | |
| Write | w | 2 | 7 |
| Execute | x | 1 |
Example Group Permissions Breakdown #
| Permission | Symbol | Value | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Read | r | 4 | |
| Write or Edit | w | 2 | 6 |
| No Permission | - | 0 |
Example Other Permissions Breakdown #
| Permission | Symbol | Value | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Read | r | 4 | |
| No Permission | - | 0 | 5 |
| Execute | x | 1 |
Log Parsing Commands #
From ByteByteGo
| GREP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
$grep<pattern>file.log |
1. | find file names that match | $grep -l"bytebytego" *.log |
4. | invert matches | $grep -v"bytebytego" test.log |
| GREP searches any given input files, selecting lines that match one or more patterns | 2. | case insensitive word match | $grep -wi"bytebytego" test.log |
5. | take patterns from a file | $grep -f pattern.txt test.log |
| 3. | show line numbers | $grep -n"bytebytego" test.log |
6. | search recursively in a dir | $grep -R"bytebytego"/home |
| CUT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
$cut -d", " -f 3 file.log |
1. | cut first 3 bytes | $cut -b 1,2,3 file.log |
3. | specify characters position | $cut -c 1-8 test.log |
| CUT cuts out selected portions of each line from each file and writes them to the standard output | 2. | select 2nd column delimited by a space | $cut -d" " -f 2 test.log |
| SED | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
$sed s/<regex>/<replace>/g |
1. | substitute a string | $sed s/bytebytego/go/g test.log |
4. | replace string on a range of lines | $sed '2-4 s/bytebytego/go/' test.log |
| SED reads the specified files, modifying the input as specified by a list of commands | 2. | replace the 2nd occurrence | $sed s/2/bytebytego/go/2 test.log |
5. | delete a line | $sed '4d' test.log |
| 3. | replace string on the 4th line | $sed '4 s/bytebytego/go/' test.log |
| AWK | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
$awk{print $4} test.log |
1. | print matched lines | $awk '/bytebytego/ {print}' test.log |
4. | print lines with more than 10 characters | $awk 'length($0)>10' test.log |
| AWK scans each input file for lines that match any of a set of patterns | 2. | split a line into fields | $awk '{print $1,$3}' test.log |
5. | find a string in a column | $awk '{if($4=="byte" print $0;}' test.log |
| 3. | print lines 2 to 7 | $awk 'NR>=2, NR<=7' (print NR, $0)' test.log |
| SORT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
$sort test.log |
1. | output to a file | $sort -o output.txt input.txt |
4. | sort based on the 3rd column | $sort -k 3n test.log |
| SORT sorts text and binary files by lines | 2. | sort in reverse order | $sort -r test.log |
5. | check if a file is ordered | $sort -c test.log |
| 3. | sort numerically | $sort -n test.log |
6. | sort and remove duplicates | $sort -u test.log |
| UNIQ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
$uniq test.log |
1. | tell how many times a line is repeated | $uniq -c test.log |
4. | skip the first two fields | $uniq -f 2 test.log |
| UNIQ reads the specified input file comparing adjacent lines, and writes a copy of each unique input line to the output file | 2. | print repeated lines | $uniq -d test.log |
5. | compare case-insensitive | $uniq -i test.log |
| 3. | print unique lines | $uniq -u test.log |
Retry a commands in shell scripts #
for i in {1..5}; do n 18 && break || sleep 15; done
Convert file contents to base64 #
base64 -w 0 "<INPUT_FILE>" > "<OUTPUT_FILE>"